Jupyter Notebooks
Contents
Jupyter Notebooks#
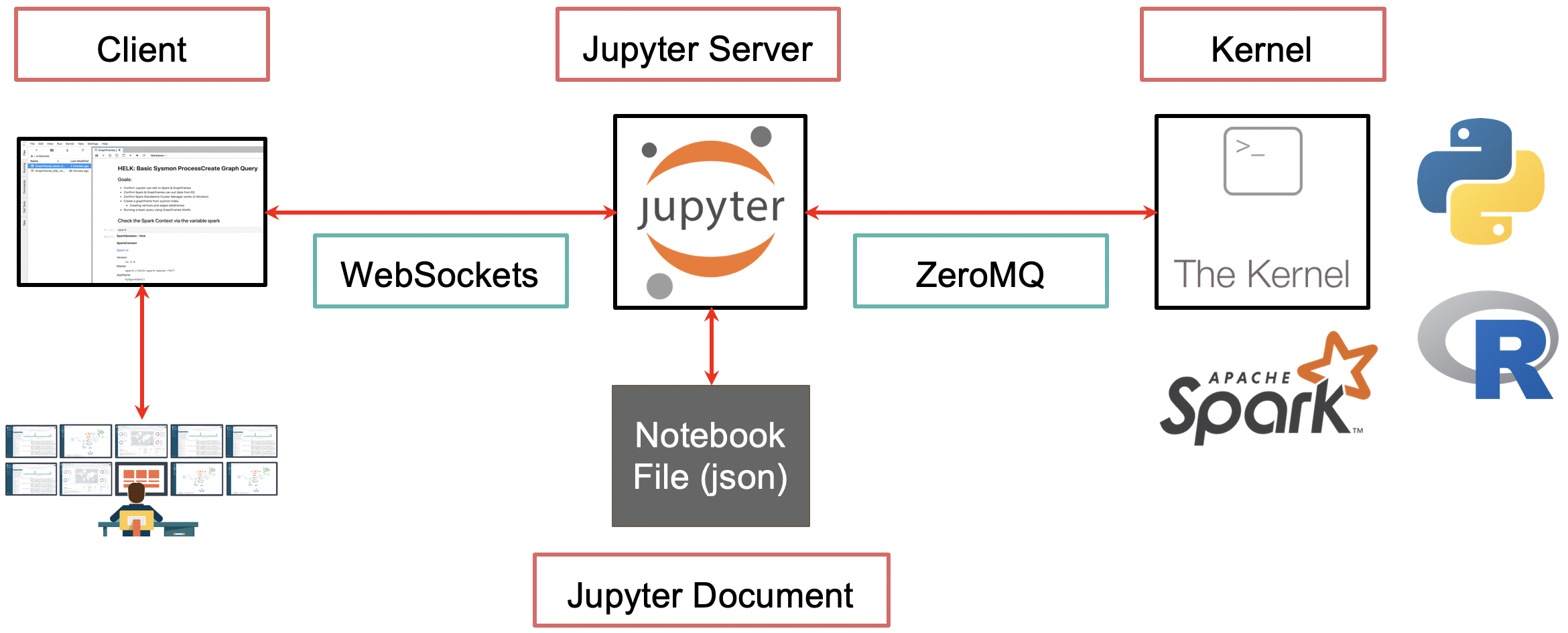
The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Uses include: data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, and much more.
Requirements#
Docker CE : Docker Community Edition (CE) is ideal for developers and small teams looking to get started with Docker and experimenting with container-based apps.
Install Jupyter Notebook Server#
You can simply download and run a docker image already created by the OTR Community. The Docker images are under the following account: https://hub.docker.com/u/cyb3rward0g. Look for the docker image names that start with jupyter-. If we want to download and run the jupyter-base image, you can do it with the following command:
$ docker run -p 8888:8888 cyb3rward0g/jupyter-base:latest
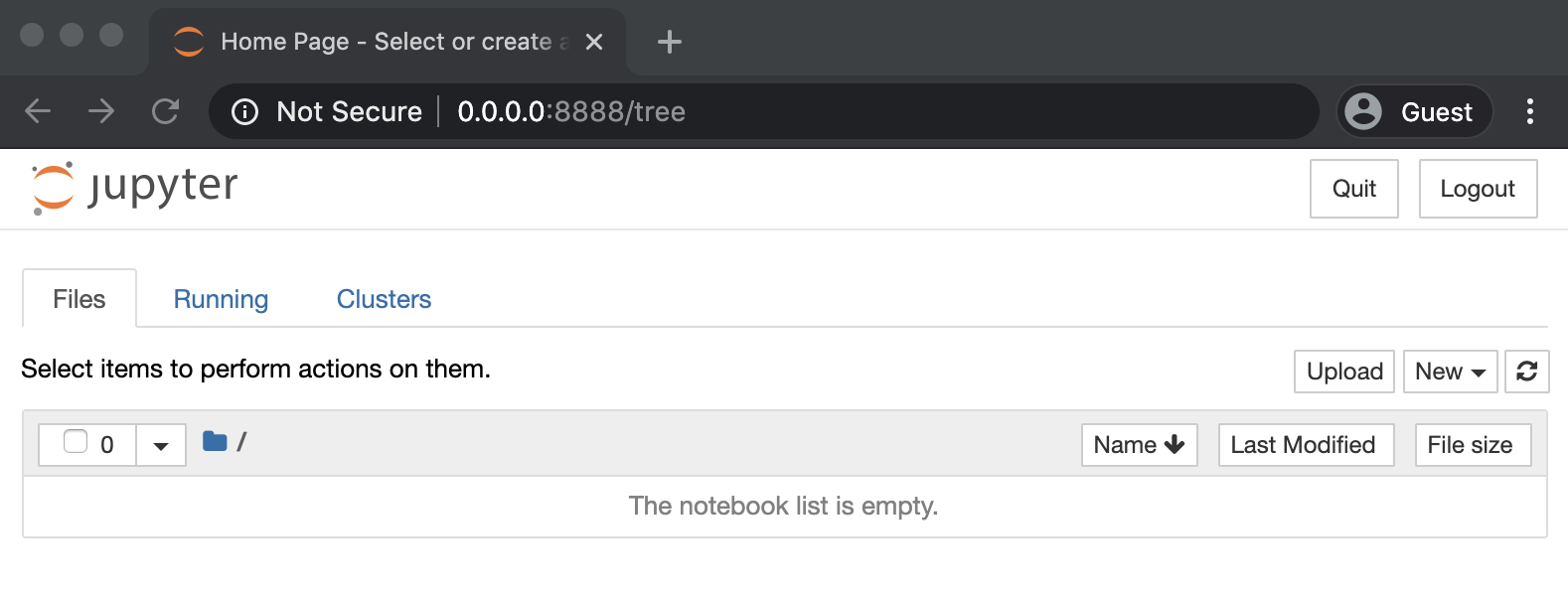
Get Notebook Server Link#
docker exec -i jupyter-base jupyter notebook list
Currently running servers:
http://0.0.0.0:8888/?token=bcd90816a041fa1f966829d1d46027e4524f40d97b96b8e0 :: /opt/jupyter/notebooks
Browse to Link#
Download Security Datasets#
Now that you have a jupyter notebook server up and running, we can download and decompress our dataset inside of the notebook. You can simply click on the first cell in your Jupyter Notebook interface and run the following command:
! curl -LJO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OTRF/Security-Datasets/master/datasets/small/windows/lateral_movement/host/covenant_wmi_wbemcomn_dll_hijack.zip
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 605k 100 605k 0 0 3522k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 3522k
Next, decompress the specific security dataset (Remember to run this in your Jupyter Notebook interface)
! unzip covenant_wmi_wbemcomn_dll_hijack.zip
Archive: covenant_wmi_wbemcomn_dll_hijack.zip
inflating: covenant_wmi_wbemcomn_dll_hijack_2020-10-09173318.json
Explore as a Dataframe#
Now, we can simply use python libraries such as Pandas to read our JSON file to a dataframe (Remember to run this in your Jupyter Notebook interface)
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_json('covenant_wmi_wbemcomn_dll_hijack_2020-10-09173318.json')
df.head(1)
Run a basic query to get Sysmon EventID 1 (ProcessCreate) events (Remember to run this in your Jupyter Notebook interface)
(
df[['Hostname','Channel','EventTime','EventID','CommandLine']]
.assign(CommandLineLength = df['CommandLine'].str.len())
[(df['Channel'] == 'Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational') & (df['EventID'] == 1)]
.head(5)
)